Ectopic Pregnancy (Part One)
Definition
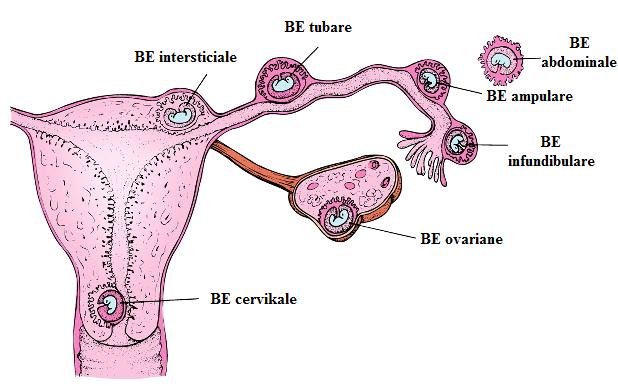
An ectopic pregnancy is the result of a deficiency in the reproductive system's physiology that allows the conceptus to implant and mature outside the endometrial cavity, which ends in fetal death and becomes a dangerous situation for the woman's life when diagnosis and treatment are delayed. Ectopic, from Greek, means out of place. An ectopic pregnancy is the implantation of the fertilized egg outside the uterine cavity, in the tubes in 97.7%, cervix, ovaries, cornua, abdomen. In the tubes, ampulla 80%, isthmus 12%, fimbriae 5%, cornua 2%, interstitial 2-3%.
Epidemiology
In the USA, in 1970, the ectopic pregnancy occurred 4.5 cases per 1000 pregnancies. Today the frequency has increased sixfold. It occurs 1 case in 40 pregnancies or 25 cases per 1000 pregnancies. Ectopic pregnancy accounts for 1-2% of all pregnancies. Maternal mortality is higher in the black race by 8% and in the white race by 4%.
- Risk Factors
- Maternal age over 35 years.
- History of pelvic, abdominal surgery, multiple abortions.
- History of PID, endometriosis.
- Conception occurring despite tubal ligation and IUD.
- Conception induced by fertility drugs or procedures.
- Smoking.
- Anatomical anomalies of the uterus (T-shaped, bicornuate uterus, uterine tumors, fibroids).
- Structural anomalies in the Fallopian tubes.
- Previous history of ectopic pregnancy.
- Previous history of STDs such as gonorrhea or chlamydia, more than 2 partners.
- Exposure to DES.
Causes
- There is not always a clear cause for ectopic pregnancy.
- Inflammation and damage to the Fallopian tubes from past medical conditions such as infection or surgery.
- Hormonal factors.
- Genetic anomalies.
- Birth defects.
- Medical conditions that damage the Fallopian tubes, reproductive organs.
Signs and Symptoms
- The classic clinical triad:
- Abdominal pain
- Amenorrhea
- Vaginal bleeding
In 50% of cases, patients present with all three symptoms.
- Other symptoms include:
- nausea / vomiting
- painful fetal movement
- fatigue and physical weakness
- fever
- syncope
- cardiac arrest
- Signs of a surgical emergency include:
- abdominal rigidity
- involuntary guarding
- increased tenderness
- signs of hypovolemic shock (orthostatic BP, tachycardia)
- Pelvic Examination
- The uterus may be slightly larger and softer than normal.
- Tenderness during uterine and cervical motion (suggests peritoneal inflammation)
- Adnexal mass may be palpated
- Uterine contents may be in the vagina