Lower Back Pain (Part Four)
TREATMENT
In general, the treatment of lower back pain is done with one of three categories: Medications, physiotherapy, and surgery.
Non-Surgical Treatment
Medical Advice
- Rest. Usually, 1-2 days of rest or bed regimen will alleviate severe lower back pain. Take frequent breaks throughout the day, but avoid sitting for long periods or staying in bed for a long time.
- Make all movements slowly and with control and gradually increase physical activity as tolerated
- Listen to your back: Change your daily activities so that you avoid movements that may cause further pain, especially bending forward and lifting weights, therefore it is recommended to avoid straining, carrying and lifting weights, or standing for a long time. For a few days, different sports activities should be avoided, except swimming, which in many cases helps in treating the problem.
- Applying heat
- Stretching the muscles of the lower back and those of the pelvis which is followed by applying ice or heat depending on which one feels better.

Medications. Some medications can be used to help alleviate your pain.
- Aspirin or Acetaminophen can relieve pain, with few side effects.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs like ibuprofen, voltaren, and naproxen can reduce pain and swelling.
- Muscle relaxants like Thiocolchicoside (Muscoril, Myoril, Neoflax, Muscoflex)
- Narcotic medications such as codeine or morphine can help with the pain.
- Steroids taken orally or injection in the back, can provide a high anti-inflammatory effect.
Physical Medicine.
Lower back pain can limit daily activities. Medications and physical treatments (physiotherapy) often combined together alleviate the pain sufficiently to do all the things you want to do.
Kinesiotherapy
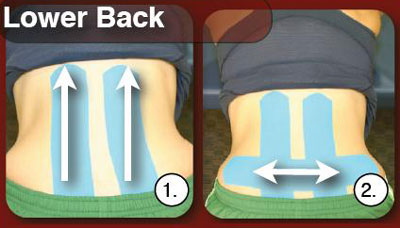
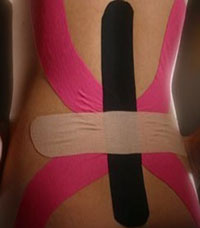
Physiotherapy may include passive modalities such as heating, ice, ultrasound, massage, and electrical stimulation. Active therapy consists of stretching exercises, weight lifting, and cardiovascular exercises. Spine exercises to restore movement and strength can be very helpful in alleviating pain.

Braces are often used. Among the most common braces is a type-corset that is placed on the back and the front part of the abdomen. Braces are not always useful, but some people report feeling more comfortable and more stable.
Chiropractic or manipulative therapy is given in many different forms. Some patients find relief from lower back pain with these treatments.
Traction is often used, but without scientific proof of effectiveness.
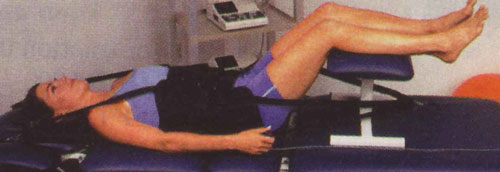
Other exercise-based programs, such as Pilates or yoga, are useful for some patients
Epidural steroid injections. In this procedure, steroids are injected into the back to reduce local inflammation.
There is good evidence that epidural injections can be successful in 42-56% of patients who have not improved with conservative (non-surgical) treatment for 6 weeks or more.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery for lower back pain should only be considered when non-surgical treatment options have been tried and failed. It is good to try non-surgical options for 6 months to a year before considering surgery.
Furthermore, surgery should only be considered if the doctor can identify the source of your pain.
Surgery is not the last treatment or option that can be done "when all other options have failed." Some patients are not candidates for surgery, even though they have significant pain and other treatments have not failed. Some types of chronic lower back pain simply cannot be treated with surgery.
Only a small percentage of patients with lumbar disc herniation require surgery. Spine surgery is usually recommended only after a period of non-surgical treatment when painful symptoms do not ease.
Microdiscectomy. The most common surgical procedure for lumbar disc herniation is lumbar microdiscectomy. Microdiscectomy involves removing the herniated or slipped part of the disc and any other fragments that are pressing on the spinal nerves.
Spinal Fusion. This is essentially a "welding" process. The basic idea is to fuse together the painful vertebrae so that they heal into a single, solid bone.
Spinal Fusion eliminates motion between the vertebrae. This is an option when motion is the source of pain. For example, the doctor may recommend spinal fusion if you have spinal instability, a severe curve (scoliosis), or severe degeneration of one or more of the discs. The theory is that if the painful spinal segments do not move, they should not hurt.
Lumbar spine fusions have been performed for decades. A variety of surgical techniques have evolved. In most cases, a bone graft is used to fuse the vertebrae. Screws, rods, or a "cage" are used to keep the spine stable while the bone graft heals.
The surgery can be done through the abdomen, on your side, back, or a combination of these. There is also a procedure that is done through a small opening near the hip. No procedure has been proven to be better than another.
The results of spinal fusion for lower back pain vary. It can be very effective in eliminating pain, may not remove the pain, and something in between. Full recovery may take more than a year.
Disc Replacement. This procedure involves removing the disc and replacing it with an artificial part, similar to knee or hip replacements (prosthetics).
The goal of disc replacement is to allow the spinal segments to retain some flexibility and to preserve more normal movement.
The surgery is done through the abdomen usually on the two lowest discs of the back
I think that the description by the group of co-authors is readable for the interested parties. Thank you for your information
Sent by Anesti Pina, më 13 September 2013 në 10:36
Hello, I am Petriti. I had a problem with my back 5 years ago, which was a result of the work I did laying tiles, during which I spent almost 40 days barely able to get in and out of a car. However, it passed after I accidentally pulled an electrical cable with a lot of force, and the pain immediately subsided, and I haven't felt it since for 5 years. But today, I lifted a weight of almost 10 kg and my back started hurting again, making it hard for me to move. Please tell me some way to relieve this pain, Petriti
Sent by Petrit Zefi, më 30 October 2013 në 03:30
Petrit, I have had the same problem with the tiles after doing a lot of physiotherapy, the pain wouldn't go away, and it even gripped my leg. In 2010, I had surgery in Athens, and now I am much better, I don't have leg pain. Sometimes, when I work for extended hours, it hurts again, but after a short rest, the pain goes away. If you have leg pain or numbness in your fingers, I advise you to visit a neurosurgeon as soon as possible before the nerve weakens. You might need surgery for the operation to be 96% successful; the nerve shouldn't lose the strength of the leg, it's a matter of time
Sent by shkelzen, më 09 January 2014 në 16:09
I am Gjergji and I have been suffering from back pain for 4 months, I have numbness in my left buttock and I always feel it on the same side. Please give me some advice on how to get it to pass, thank you
Sent by gjergji, më 10 December 2014 në 07:56