Fatty Liver (Hepatosteatosis, Steatohepatitis) (Part Two)
Causes
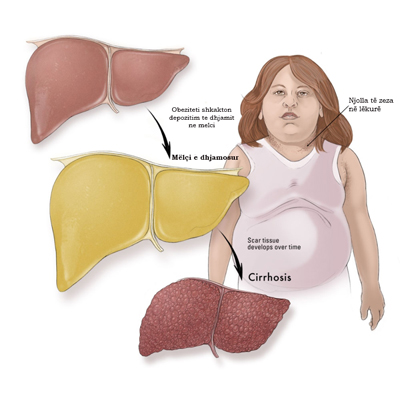
There are various different situations, medications, and toxic substances (poisons) that cause fat deposition in the liver. Consuming high-calorie foods leads to fat accumulation in the liver. Certain conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and high triglycerides cause fat deposition in the liver. Patients at higher risk for fatty liver are those of middle age and overweight.
Some causes of fatty liver are:
- Excessive use of alcohol.
- Poor nutrition.
- Use of steroids.
- Toxicity from Valproic acid.
- Obesity.
- Cushing syndrome.
- Poisons
- Taking tetracycline in high doses.
- Pregnancy
- Diabetes
- Hyperlipidemia.
- Rapid weight loss.
Some people develop fatty liver without having any of the aforementioned conditions.
Symptoms (Signs)
Fatty liver can be diagnosed with blood tests and also with a liver biopsy. It is one of the most common reasons for a slight increase in liver enzyme levels. Special imaging taken from ultrasounds, scanners, magnetic resonance can suggest fatty liver but a biopsy is necessary to confirm it.
Biopsy is the technique of taking some cells from the liver, a procedure that is done with a special needle. Then, the taken cells are examined under a microscope by a specialist doctor.
Treatment
Fatty liver often does not cause problems. In these cases, it is called asymptomatic.
Weight loss, limiting fats, and exercise in overweight patients produce sustainable results over time so efforts should be made. Fatty liver caused by alcohol toxicity may not improve even if its use is discontinued.
Good control of diabetes can reduce fatty liver. You should lower your triglyceride levels with diet, medication, or both together. Eat in a healthy and balanced way.
Increase your physical activity.
Have regular periodic check-ups with a liver specialist doctor.
There are no medical or surgical treatments for fatty liver or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), but improving your diet and increasing physical activity can help in preventing or reversing some of the damages.
Progression
Fatty liver may not cause damage or may lead to liver infections. This condition is called steatohepatitis.
When it is associated with alcohol abuse it is called alcoholic steatohepatitis. Often it is not related to alcohol and is called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Over time, the liver is severely damaged, this situation is called cirrhosis.
Hepatic cirrhosis is a serious situation that leads to liver dysfunction. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis is one of the causes of hepatic cirrhosis.