Redness - Facial Redness
Facial redness is temporary, caused by various factors such as emotional discomfort in different social situations, alcohol consumption, eating spicy foods, or changes in the ambient temperature where we are, high temperature. All these factors cause an increase in the amount of blood circulating in the skin and make the face redder. Avoiding these factors can reduce facial redness.
Other facial redness results from skin diseases like Seborrheic Dermatitis or Rosacea, a pathology that is becoming increasingly common, especially in the third and fourth decades of life.
Rosacea: Facial redness in Rosacea pathology includes the cheeks, nose, and forehead and develops gradually. It starts as a mild, persistent facial redness that does not depend on the temporary redness factors mentioned above and in many cases looks like sunburn. However, while the initial facial redness may vary from day to day, the redness from rosacea progressively worsens: In addition to the initial facial redness, the blood capillaries (telangiectasias) become more pronounced and visible.
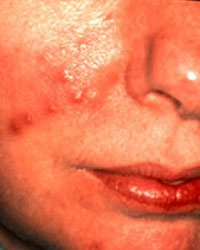
In progressive Rosacea, the capillaries (telangiectasias) continuously widen and become more pronounced, and then small papules and pustules with pus tips begin to appear, leading to aesthetic and medical problems. A constantly red face is an unpleasant sight and causes those who have it to suffer from having unhealthy skin.
Below are some steps that help reduce skin redness.
Avoiding prolonged exposure to the sun and using sunscreen with a high protective filter (up to 50+) every day and when you are exposed to the sun every 3 hours.
- Avoid long exposures to hot environments.
- Try to reduce stress. Deep breathing helps to normalize heartbeats in stressful situations and to cope more calmly with these situations, yoga, or other relaxation techniques provide significant help in such stressful conditions.
- Avoid consuming spicy foods, alcohol, and hot drinks.
- Avoid hot baths or saunas, or indiscriminate use of skin care products.
- Immediately consult your dermatologist for treatment of the pathology so it does not become chronic.
Rosacea is a pathology that does not pose a medical risk and can usually be controlled with treatment. However, if not treated in time, it can be persistent and chronic, in these cases there are permanent changes in appearance (permanent redness) which cause patients to feel bad about their condition due to their appearance. They begin to avoid social contacts and engagements, all of which lead to a loss of self-respect and significant psychological harm.
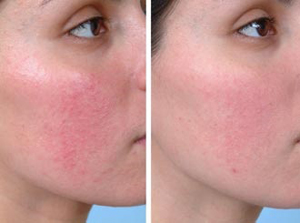
Medical Treatment
Medical treatment consists in the use of antibiotics orally and locally. This treatment lasts and must be done under the care of a dermatologist.
Nowadays, the use of modern techniques such as laser therapy has made it possible to eliminate fine capillaries on the face (telangiectasias), and the aesthetic and moral benefit is quite high.
Photo on the right: Results of Rosacea treatment with systemic and local antibiotics
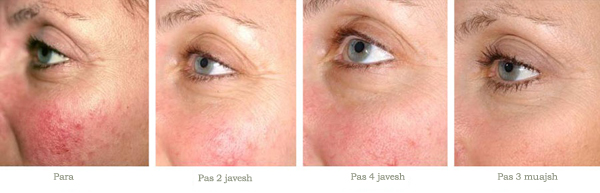
Photo above: Treatment of rosacea with laser.
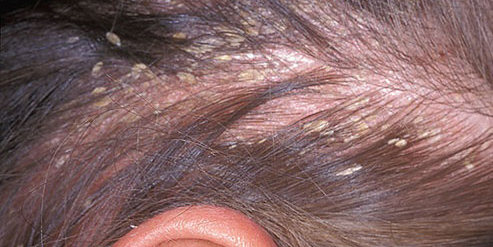
Seborrheic Dermatitis: Another fairly common pathology that is accompanied by facial skin redness and in a higher percentage in men is seborrheic dermatitis, an inflammatory skin disease that comes with redness, itching, fine scales, and seborrhea on the face and scalp (what is called dandruff), and even on the body.
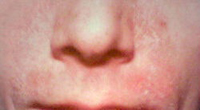
People who have this pathology are often embarrassed in social environments because of their red, oily face covered with fine scales (white skin flakes similar to dandruff), this pathology is more localized in what is called the T-zone on the face where most of the oil glands are.
Sun exposure seems to improve this pathology, while medical treatment consists in the use of ointments containing ketoconazole or ciclopirox (antifungal components), the use of weak corticosteroid ointments should be done under the care of a dermatologist and only for a short period during the exacerbation phases of the pathology, the use of itraconazole, ketoconazole, or fluconazole (antifungal drugs) systemically for severe forms of the pathology is quite effective, while scalp dandruff is treated with the use of shampoos that contain Selenium sulfide (2.5%), ketoconazole, ciclopirox, salicylic acid, tar, selenium, sulfur, or zinc.
Hello, I am a 22-year-old girl and I have a problem with blushing, and I kindly ask you to give me advice on how to get rid of it
Sent by detkaa@hotmail.com, më 07 July 2013 në 07:11
Thank you for the information. Please, what foods should not be consumed when we have this pathology?
Sent by Emanuela, më 10 March 2014 në 13:55
Hello, I am a 19-year-old girl. I have redness on my cheeks, please find me a piece of advice to get rid of this
Sent by tuba, më 05 December 2014 në 07:45