Gallstones (Part One)
What are gallstones?
Gallstones form when the fluid accumulated in the gallbladder thickens or solidifies into small pieces of material similar to stones. The fluid, called bile (gallbladder fluid) helps in the digestion of food fats. Bile is produced in the liver, then stored in the gallbladder until the body needs it for the digestion of fats. At this time, the gallbladder contracts, pushing the bile into a tube called the common bile duct from which the bile passes into the small intestine, aiding in the digestion of food.
Bile contains water, cholesterol, fats, bile salts, proteins, and bilirubin. Bile salts break down fats, while bilirubin gives feces (stool) its yellow color. If the bile contains too much cholesterol, bile salts, or bilirubin, under certain conditions, stones can form.
There are two types of gallstones: Cholesterol stones and pigment stones.
- Cholesterol stones are usually yellow-green in color and are primarily made of hardened cholesterol. 80% of gallstones are of this nature.
- Pigment stones are small, dark-colored, and made of bilirubin.
Gallstones can range in size from as small as grains of sand to as large as a golf ball. The gallbladder can form a single large stone, hundreds of small stones, or any possible combination of the two. Stones can block the normal flow of bile (gallbladder fluid) if they lodge in any of the ducts through which bile flows from the liver to the small intestine. These places can be:
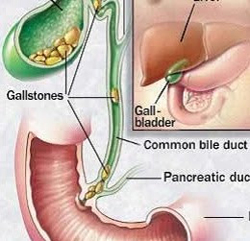
the hepatic ducts which take the bile out of the liver, the cystic duct, through which bile goes in and out of the gallbladder, and the common bile duct which carries bile from the cystic and hepatic ducts into the small intestine.
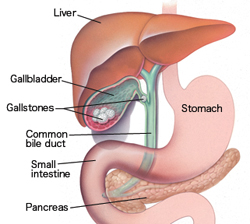
Bile remains in these ducts causing infection of the gallbladder, the duct itself, and rarely the liver. Another duct that drains into the hepatic bile duct is the pancreatic duct, which releases digestive enzymes from the pancreas.
If stones block the exit of this duct, the digestive enzymes remain in the pancreas causing a very painful inflammation called pancreatitis from gallstones. If any of these ducts remain blocked for a certain period, significant or fatal damage, or infection can affect the gallbladder, liver, or pancreas.
Warning signs of this serious situation include:
- high temperature,
- jaundice of the skin and persistent pain
What causes gallstones?
Cholesterol stones
Scientists believe that cholesterol stones form when bile contains too much cholesterol, too much bilirubin, or not enough bile salts, or when the gallbladder does not empty completely for various reasons.
Pigment stones
The cause of these stones is unclear. They are likely to form in people who have: liver cirrhosis, infection of the biliary tract, inherited blood diseases (such as sickle cell anemia where the body produces too much bilirubin). Other factors are thought to cause the production of many stones from the presence of a single gallstone.
However, other factors that influence the formation of gallstones, particularly cholesterol stones, have been discovered.
Obesity.
It is a risk factor for creating stones, especially in women. A comprehensive study has shown that even being slightly overweight increases the risk of developing gallstones. This happens because obesity may reduce the amount of bile salts in bile, leading to a higher concentration of cholesterol in it. Obesity also reduces the ability of the gallbladder to empty.
Estrogen (female hormone).
The increased amount of estrogen during pregnancy, hormone replacement therapy, and when taking oral contraceptives, increases the level of cholesterol in bile and reduces the movements of the gallbladder. Both these factors together lead to the formation of stones.
Ethnicity.
We do not have accurate data regarding the population of Albania.
Gender.
Women aged 20 to 60 years are twice as likely to develop gallstones as men. Age. People over the age of 60 are more likely to develop gallstones than younger people.
Medications to lower cholesterol levels.
Medications used to lower blood cholesterol levels increase the amount of cholesterol secreted into bile. As a result, the risk of forming gallstones increases. Diabetes.
In general, people with diabetes have high levels of fatty acids called triglycerides. These types of fatty acids increase the risk of forming gallstones.
Rapid weight loss.
As the body breaks down fats during rapid weight loss, the liver secretes more cholesterol into bile, leading to the formation of stones. Fasting. Reduces the mobility of the gallbladder causing over-concentration of bile with cholesterol, leading to the formation of stones.
please help me with the procedure during the operation, whether it is better to have surgery with laparoscopy or with open surgery
Sent by caush, më 04 November 2014 në 12:19
I AM VERY RELIEVED BY THIS INFORMATION THAT I RECEIVED.
THANK YOU, BUT I AM CURIOUS TO KNOW IN MORE DETAIL ABOUT THE LAPAROSCOPY PROCEDURE
Sent by caush, më 04 November 2014 në 12:48
Information is more than half of health!
Sent by hamdi, më 30 June 2017 në 02:47